Procedural Caves - Cellular Automata#
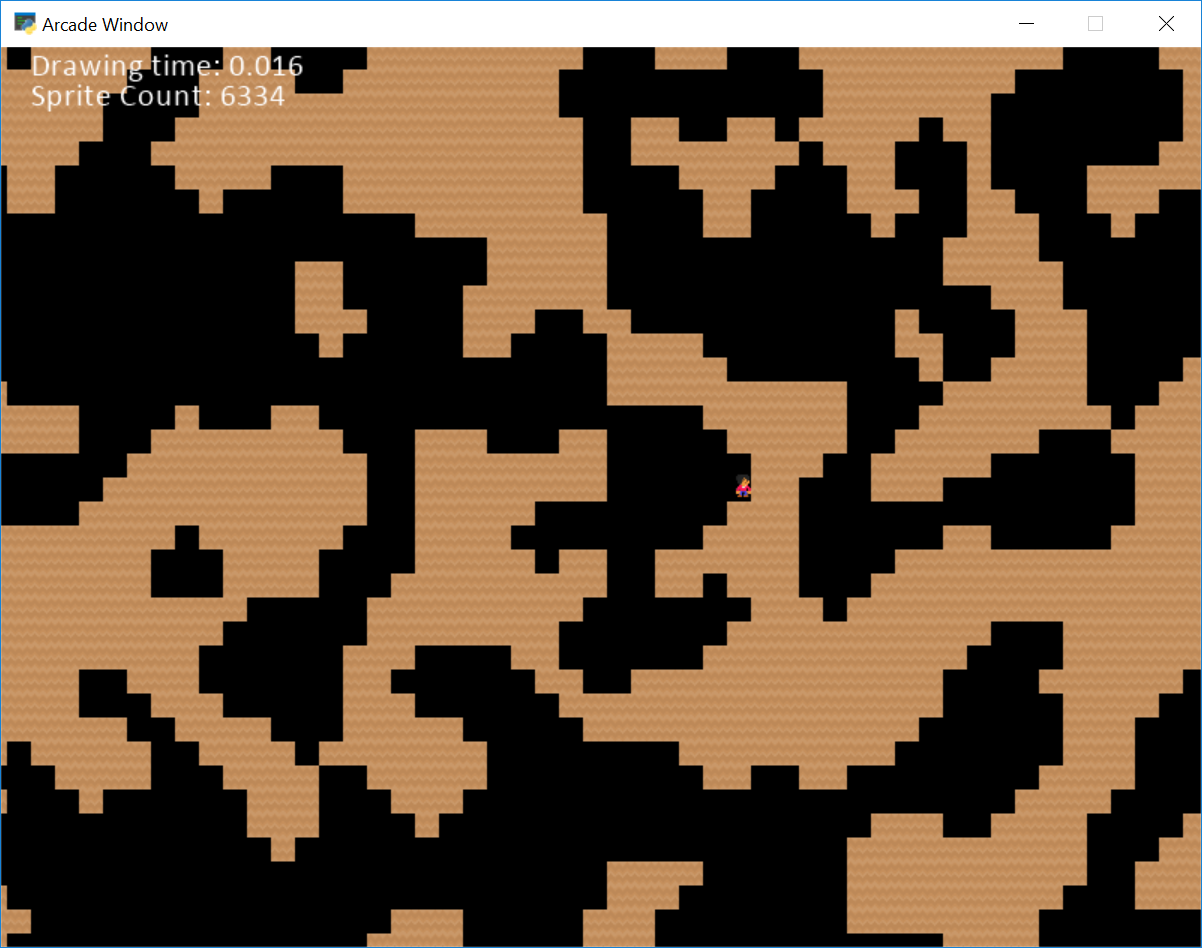
procedural_caves_cellular.py#
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 | """
This example procedurally develops a random cave based on cellular automata.
For more information, see:
https://gamedevelopment.tutsplus.com/tutorials/generate-random-cave-levels-using-cellular-automata--gamedev-9664
If Python and Arcade are installed, this example can be run from the command line with:
python -m arcade.examples.procedural_caves_cellular
"""
import random
import arcade
import timeit
from pyglet.math import Vec2
# Sprite scaling. Make this larger, like 0.5 to zoom in and add
# 'mystery' to what you can see. Make it smaller, like 0.1 to see
# more of the map.
SPRITE_SCALING = 0.25
SPRITE_SIZE = 128 * SPRITE_SCALING
# How big the grid is
GRID_WIDTH = 450
GRID_HEIGHT = 400
# Parameters for cellular automata
CHANCE_TO_START_ALIVE = 0.4
DEATH_LIMIT = 3
BIRTH_LIMIT = 4
NUMBER_OF_STEPS = 4
# How fast the player moves
MOVEMENT_SPEED = 5
# How close the player can get to the edge before we scroll.
VIEWPORT_MARGIN = 300
# How big the window is
WINDOW_WIDTH = 800
WINDOW_HEIGHT = 600
WINDOW_TITLE = "Procedural Caves Cellular Automata Example"
# How fast the camera pans to the player. 1.0 is instant.
CAMERA_SPEED = 0.1
def create_grid(width, height):
""" Create a two-dimensional grid of specified size. """
return [[0 for _x in range(width)] for _y in range(height)]
def initialize_grid(grid):
""" Randomly set grid locations to on/off based on chance. """
height = len(grid)
width = len(grid[0])
for row in range(height):
for column in range(width):
if random.random() <= CHANCE_TO_START_ALIVE:
grid[row][column] = 1
def count_alive_neighbors(grid, x, y):
""" Count neighbors that are alive. """
height = len(grid)
width = len(grid[0])
alive_count = 0
for i in range(-1, 2):
for j in range(-1, 2):
neighbor_x = x + i
neighbor_y = y + j
if i == 0 and j == 0:
continue
elif neighbor_x < 0 or neighbor_y < 0 or neighbor_y >= height or neighbor_x >= width:
# Edges are considered alive. Makes map more likely to appear naturally closed.
alive_count += 1
elif grid[neighbor_y][neighbor_x] == 1:
alive_count += 1
return alive_count
def do_simulation_step(old_grid):
""" Run a step of the cellular automaton. """
height = len(old_grid)
width = len(old_grid[0])
new_grid = create_grid(width, height)
for x in range(width):
for y in range(height):
alive_neighbors = count_alive_neighbors(old_grid, x, y)
if old_grid[y][x] == 1:
if alive_neighbors < DEATH_LIMIT:
new_grid[y][x] = 0
else:
new_grid[y][x] = 1
else:
if alive_neighbors > BIRTH_LIMIT:
new_grid[y][x] = 1
else:
new_grid[y][x] = 0
return new_grid
class InstructionView(arcade.View):
""" View to show instructions """
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.frame_count = 0
def on_show_view(self):
""" This is run once when we switch to this view """
arcade.set_background_color(arcade.csscolor.DARK_SLATE_BLUE)
# Reset the viewport, necessary if we have a scrolling game and we need
# to reset the viewport back to the start so we can see what we draw.
arcade.set_viewport(0, self.window.width, 0, self.window.height)
def on_draw(self):
""" Draw this view """
self.clear()
arcade.draw_text("Loading...", self.window.width / 2, self.window.height / 2,
arcade.color.BLACK, font_size=50, anchor_x="center")
def on_update(self, dt):
if self.frame_count == 0:
self.frame_count += 1
return
""" If the user presses the mouse button, start the game. """
game_view = GameView()
game_view.setup()
self.window.show_view(game_view)
class GameView(arcade.View):
"""
Main application class.
"""
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.grid = None
self.wall_list = None
self.player_list = None
self.player_sprite = None
self.draw_time = 0
self.processing_time = 0
self.physics_engine = None
# Track the current state of what key is pressed
self.left_pressed = False
self.right_pressed = False
self.up_pressed = False
self.down_pressed = False
# Create the cameras. One for the GUI, one for the sprites.
# We scroll the 'sprite world' but not the GUI.
self.camera_sprites = arcade.Camera(self.window.width, self.window.height)
self.camera_gui = arcade.Camera(self.window.width, self.window.height)
arcade.set_background_color(arcade.color.BLACK)
self.sprite_count_text = None
self.draw_time_text = None
self.processing_time_text = None
def setup(self):
self.wall_list = arcade.SpriteList(use_spatial_hash=True)
self.player_list = arcade.SpriteList()
# Create cave system using a 2D grid
self.grid = create_grid(GRID_WIDTH, GRID_HEIGHT)
initialize_grid(self.grid)
for step in range(NUMBER_OF_STEPS):
self.grid = do_simulation_step(self.grid)
# Create sprites based on 2D grid
# Each grid location is a sprite.
for row in range(GRID_HEIGHT):
for column in range(GRID_WIDTH):
if self.grid[row][column] == 1:
wall = arcade.Sprite(":resources:images/tiles/grassCenter.png", SPRITE_SCALING)
wall.center_x = column * SPRITE_SIZE + SPRITE_SIZE / 2
wall.center_y = row * SPRITE_SIZE + SPRITE_SIZE / 2
self.wall_list.append(wall)
# Set up the player
self.player_sprite = arcade.Sprite(":resources:images/animated_characters/female_person/"
"femalePerson_idle.png",
SPRITE_SCALING)
self.player_list.append(self.player_sprite)
# Randomly place the player. If we are in a wall, repeat until we aren't.
placed = False
while not placed:
# Randomly position
max_x = int(GRID_WIDTH * SPRITE_SIZE)
max_y = int(GRID_HEIGHT * SPRITE_SIZE)
self.player_sprite.center_x = random.randrange(max_x)
self.player_sprite.center_y = random.randrange(max_y)
# Are we in a wall?
walls_hit = arcade.check_for_collision_with_list(self.player_sprite, self.wall_list)
if len(walls_hit) == 0:
# Not in a wall! Success!
placed = True
self.scroll_to_player(1.0)
self.physics_engine = arcade.PhysicsEngineSimple(self.player_sprite,
self.wall_list)
# Draw info on the screen
sprite_count = len(self.wall_list)
output = f"Sprite Count: {sprite_count:,}"
self.sprite_count_text = arcade.Text(output,
20,
self.window.height - 20,
arcade.color.WHITE, 16)
output = "Drawing time:"
self.draw_time_text = arcade.Text(output,
20,
self.window.height - 40,
arcade.color.WHITE, 16)
output = "Processing time:"
self.processing_time_text = arcade.Text(output,
20,
self.window.height - 60,
arcade.color.WHITE, 16)
def on_draw(self):
""" Render the screen. """
# Start timing how long this takes
draw_start_time = timeit.default_timer()
# This command should happen before we start drawing. It will clear
# the screen to the background color, and erase what we drew last frame.
self.clear()
# Select the camera we'll use to draw all our sprites
self.camera_sprites.use()
# Draw the sprites
self.wall_list.draw()
self.player_list.draw()
# Select the (unscrolled) camera for our GUI
self.camera_gui.use()
self.sprite_count_text.draw()
output = f"Drawing time: {self.draw_time:.3f}"
self.draw_time_text.text = output
self.draw_time_text.draw()
output = f"Processing time: {self.processing_time:.3f}"
self.processing_time_text.text = output
self.processing_time_text.draw()
self.draw_time = timeit.default_timer() - draw_start_time
def update_player_speed(self):
# Calculate speed based on the keys pressed
self.player_sprite.change_x = 0
self.player_sprite.change_y = 0
if self.up_pressed and not self.down_pressed:
self.player_sprite.change_y = MOVEMENT_SPEED
elif self.down_pressed and not self.up_pressed:
self.player_sprite.change_y = -MOVEMENT_SPEED
if self.left_pressed and not self.right_pressed:
self.player_sprite.change_x = -MOVEMENT_SPEED
elif self.right_pressed and not self.left_pressed:
self.player_sprite.change_x = MOVEMENT_SPEED
def on_key_press(self, key, modifiers):
"""Called whenever a key is pressed. """
if key == arcade.key.UP:
self.up_pressed = True
elif key == arcade.key.DOWN:
self.down_pressed = True
elif key == arcade.key.LEFT:
self.left_pressed = True
elif key == arcade.key.RIGHT:
self.right_pressed = True
def on_key_release(self, key, modifiers):
"""Called when the user releases a key. """
if key == arcade.key.UP:
self.up_pressed = False
elif key == arcade.key.DOWN:
self.down_pressed = False
elif key == arcade.key.LEFT:
self.left_pressed = False
elif key == arcade.key.RIGHT:
self.right_pressed = False
def scroll_to_player(self, speed=CAMERA_SPEED):
"""
Scroll the window to the player.
if CAMERA_SPEED is 1, the camera will immediately move to the desired position.
Anything between 0 and 1 will have the camera move to the location with a smoother
pan.
"""
position = Vec2(self.player_sprite.center_x - self.window.width / 2,
self.player_sprite.center_y - self.window.height / 2)
self.camera_sprites.move_to(position, speed)
self.camera_sprites.update()
def on_resize(self, width, height):
"""
Resize window
Handle the user grabbing the edge and resizing the window.
"""
self.camera_sprites.resize(int(width), int(height))
self.camera_gui.resize(int(width), int(height))
def on_update(self, delta_time):
""" Movement and game logic """
start_time = timeit.default_timer()
# Call update on all sprites (The sprites don't do much in this
# example though.)
self.update_player_speed()
self.physics_engine.update()
# Scroll the screen to the player
self.scroll_to_player()
# Save the time it took to do this.
self.processing_time = timeit.default_timer() - start_time
def main():
window = arcade.Window(WINDOW_WIDTH, WINDOW_HEIGHT, WINDOW_TITLE, resizable=True)
start_view = InstructionView()
window.show_view(start_view)
arcade.run()
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
|